Attomarker has developed a COVID-19 Antibody Immunity test which is fully CE marked and is fully quantitative referenced to the NIST standard human antibody.
The test is a fully quantitative immunoassay calibrated against the conserved S2 regions of the spike protein, omicron spike protein, nucleocapsid and receptor binding domain proteins with recombinant antibodies calibrated against the mass standard material NIST Human Antibody. ¹ ²
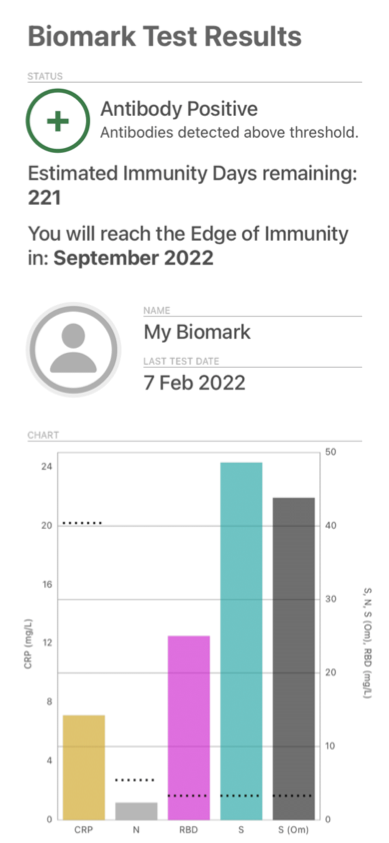
It measures the total IgG binding to:
-
N = Nucleocapsid, indicating past infection
-
S = Spike Protein, indicating past infection or vaccination
-
SO = Spike Protein from the Omicron Variant, indicating vaccine binding to the Omicron variant or past infection from Omicron
-
RBD = Receptor Binding Domain, showing antibody levels to the key part of spike protein that binds to cells during infection
The concentration of S antibodies is used to assess the number of ‘Immunity Days’ to the ‘Edge of Immunity’ calculated from an antibody half-life of 60 days and a nasal mucosa protection threshold of 3.4 mg/L, rounded to the nearest month. The half-life of antibodies ranges from 60 – 200 days ³ and is personalised which can only be determined from a paired-antibody test 3 months apart.
The test is usually sold as part of a consultation in private healthcare to patients who believe they are immuno-compromised, preparing to travel, have vulnerable relatives or considering whether to have a booster jab or not.
Omicron BA.1 Variant
There is now growing evidence from the Attomarker clinics that point to the 3.4 mg/L threshold needs to be revised upwards perhaps to 6.8 mg/L to reflect the reduced binding of the vaccine antibodies to the omicron spike protein. Consequently, the Immunity Days calculation is based on the alpha variant (the first variant for which the vaccines were developed). It may be reduced for the new omicron BA.1 variant.
N antibody levels have dominated the recovery of patients at the beginning of the pandemic and were often described as the antibody indicating previous infection. As the variants have changed, with the site of infection changing from the lungs to the upper-respiratory tract, the levels of N antibodies have reduced.
Conclusions
-
Antibody Immunity can be quantified and there is growing evidence that a threshold of 3.4 mg/L will protect against infection.
-
Antibody immunity wanes over time and this is estimated using the immunity days based on the shortest observed antibody half-life. It is the edge of immunity after which antibody levels may not be protective.
-
The assessment of “immunity days” can be made more accurate with a paired test measured 100 days apart.
-
The BA.1 variant probably shortens the days to the edge of immunity by up to 30 days.
Contact: Prof Andrew Shaw, Andrew.Shaw@attomarker.com
References
- James-Pemberton PH, Helliwell MW, Olkhov RV, et al. Fully Quantitative Measurements of the Antibody Levels for SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Vaccinations calibrated against the NISTmAb Standard IgG Antibody. medRxiv 2022: 2022.07.12.22277533.
- James-Pemberton PH, Helliwell MW, Olkhov RV, et al. Vaccine, Booster and Natural Antibody Binding to SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (BA.1) Spike Protein and Vaccine Efficacy. medRxiv 2022: 2022.07.12.22277539.
- Dan JM, Mateus J, Kato Y, et al. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science 2021; 371(6529): eabf4063.
